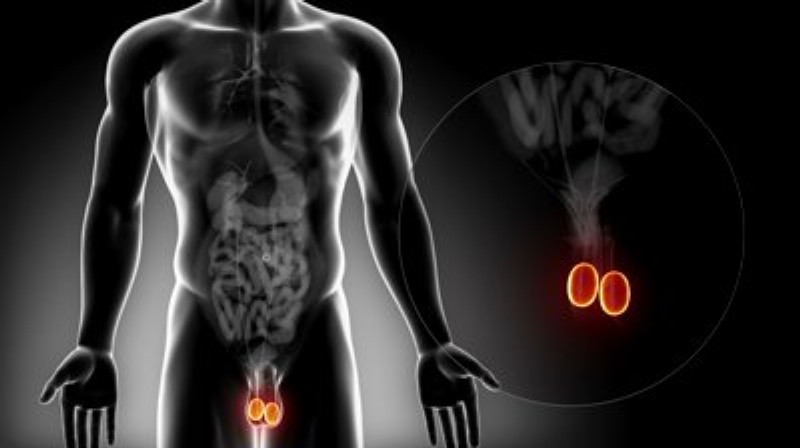
Tudtad? Bizonyos fádalomcsillapítók feltehetően károsíthatják a here működését!
A paracetamol, aszpirin és indometacin nem-szteroid gyulladáscsökkentő gyógyszerek endokrin diszruptor* vegyületként beleavatkozhatnak a here tesztoszteron előállításának folyamatába. Az ilyen gyógyszerek rendszeres és nagy dózisú szedésének pontos hatásai a hormonális működésekre még nem teljesen ismertek. A kutatók kifejezetten kiemelik az élsportolók csoportját, mint olyan csoportot akik gyakran használnak ilyen készítményeket és felmerülhet a számukra kedvezőtlen hatások lehetősége is.
Fontos, hogy gyógyszereket csak orvossal konzultálva, a ténylegesen szükséges ideig fogyasszon a sportoló!
Forrás: Albert O, Desdoits-Lethimonier C, Lesné L, Legrand A, Guillé F, Bensalah K, Dejucq-Rainsford N, Jégou B., Paracetamol, aspirin and indomethacin display endocrine disrupting properties in the adult human testis in vitro. Hum Reprod. 2013 May 12. [Epub ahead of print]
*
"Az endokrin diszruptorok az endokrin rendszerbe, azaz a belső elválasztású mirigyek működését károsító, hormonális rendszerbe beavatkozó anyagok. Például xenoösztrogének, melyek mesterséges vegyszerek, amik a szervezetbe jutva ösztrögén (női nemi hormon) hatást fejtenek ki. Az endokrin diszruptor anyagok a hormonrendszer károsításával nemcsak például elnőiesedést okozhatnak férfiaknál, hanem károsítják az ideg- és az immunrendszert; illetve több rákfajta, így a mell-, here- és prosztatarák kialakulásához is hozzájárulhatnak."
Forrás: kockazatos.hu/kislexikon/endokrin-diszruptor-anyagok-edc-k
Kép forrása: footage.shutterstock.com










Utolsó kommentek